Mollusca
– 1. Cephalopoda
–– 2.1 Cephalopoda stem groups
–– 2.2 "Nautiloidea"
–– 2.3 Ammonoidea
–– 2.4 Coleoidea
–– 2.5 Quiz ←
Test your knowledge and understanding of Class Cephalopoda by completing the quiz below.
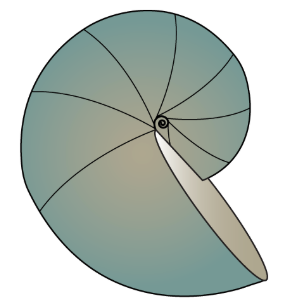
Question
Is the cephalopod shell shown above evolute, convolute, or involute?
Answer
The shell has convolute coiling because the youngest whorls partially cover earlier whorls.
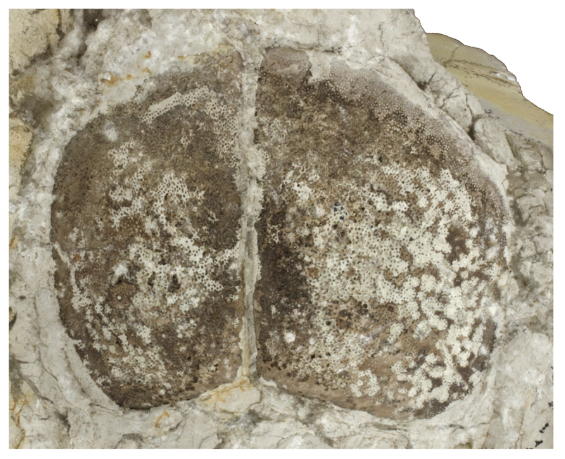

Question
What are aptychi? (See example above.)
Answer
Aptychi are paired structures that look superficially like bivalve shells. They are thought to be parts of the bodies of ammonoids, but their function(s) remain uncertain.

Question
What are the structures called that separate the internal chambers of nautiloid and ammonoid shells?
Answer
Sutures. These are relatively simple in shape in nautiloids, but much more complex in some ammonoids.
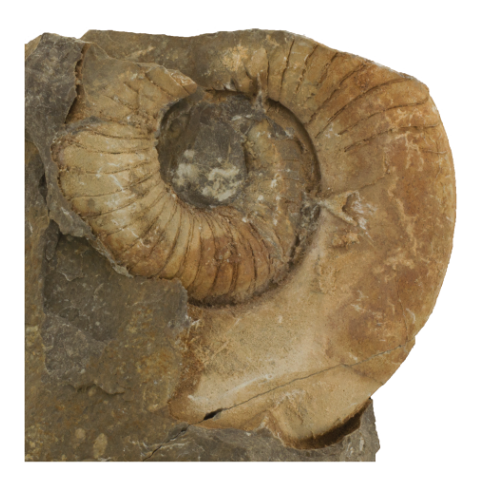

Question
Is this shell a nautiloid or an ammonoid? How do you know?
Answer
The shell is a nautiloid. Its sutures are very simple in shape. If it were an ammonoid, the sutures would be much more complex.
Question
What is the primary function ofchromatophores in modern coleoids?
Answer
Chromatophores allow coleoids to rapidly change color.

Question
What specific kind of cephalopod is shown above?
Answer
This is a baculite, a type of straight-shelled ammonite.
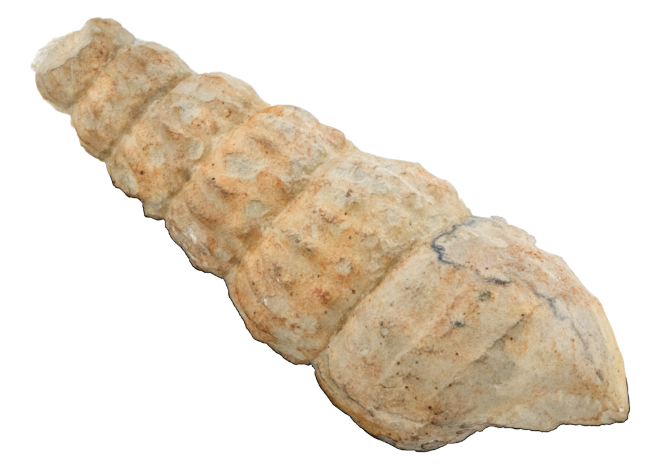

Question
Characterize the shape of the cephalopod shell above (it looks like a snail shell, but is not).
Answer
This specimen of heteromorph ammonite has a torticone shell.
Question
What quality most readily separates heteromorphs from other ammonites?
Answer
The shells of heteromorphs are irregularly coiled (as opposed to the typically planispiral shells of most ammonoids).
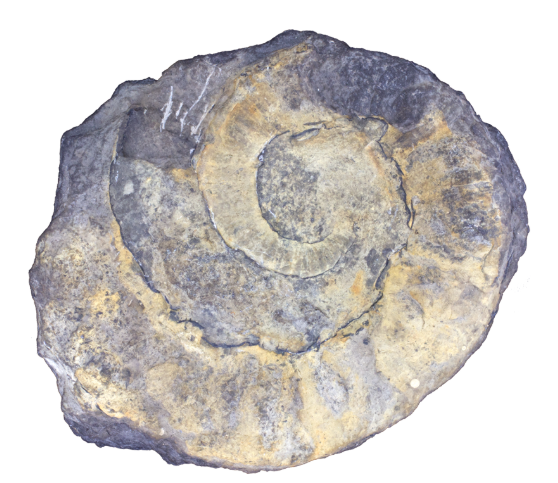

Question
Characterize the shape of the shell shown above.
Answer
The shell is a gyrocone. It is curved, but earlier whorls do not touch each other.
Question
During which geological interval did nautiloids reach their peak diversity? a) Late Paleozoic b) Triassic c) Cretaceous d) Paleogene
Answer
Nautiloids reached their peak diversity during the late Paleozoic.
Question
What is a gladius?
Answer
A gladius is an rigid internal body part found in some ancient coleoids and the modern vampire squid.
Question
What is a phragmocone?
Answer
A phragmocone comprises the chambered portions of a cephalopod shell. The remainder of the shell is occupied by the living animal and is called the body chamber.
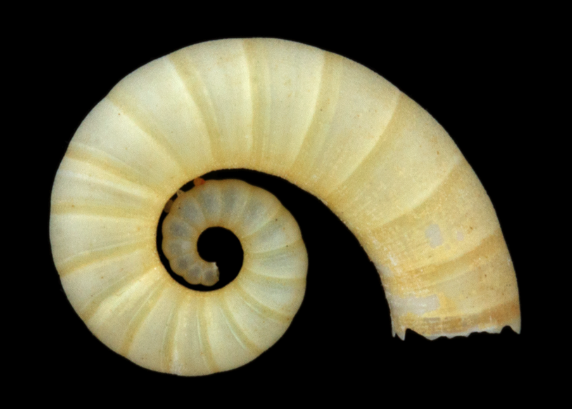

Question
What kind of modern shell is shown in the image above?
Answer
This is the Internal shell of the extant squid Spirula spirula,

Question
What kind of fossil is shown in the image above?
Answer
Beleminte. Belemintes were internal shells (guards) of squid-like animals that lived during Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
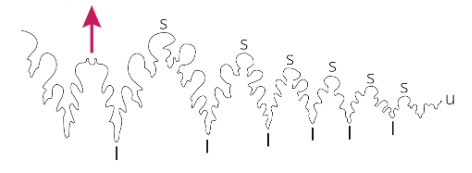
Question
If you find an ammonoid fossil with a suture pattern that looks like the one above, most likely when (what period(s)) did the ammonoid live?
Answer
This is an ammonitic suture, so the specimen is likely from either the Jurassic or Cretaceous period.
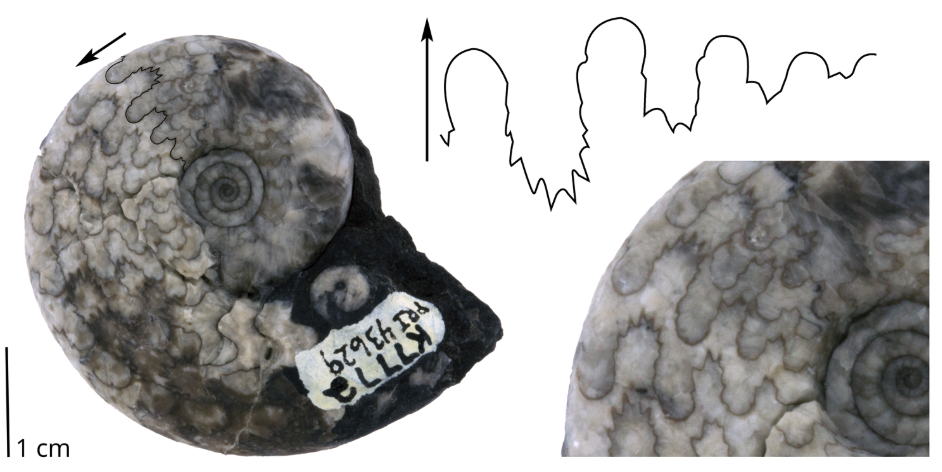

Question
During which geological period did this cephalopod most likely live?
Answer
This specimen has a ceratite suture, indicating that it is an ammonoid that probably lived during the Triassic period.
Question
Ammonoids and coleoids are both thought to have evolved from one particular group of nautiloids. What is that group?
Answer
Ammonoids and coleoids are thought to have evolved from bactritids.

Question
Characterize the shape of the shell shown above AND identify the tube-like structure that runs down the center of the shell.
Answer
The shell is an orthoconic longicone (=straight, long shell). The central tube-like structure is the siphuncle.
Question
Do members of any major group of modern Coleoidea typically have internal shells?
Answer
Yes. Cuttlefish have internal, chambered shells called "cuttlebones."
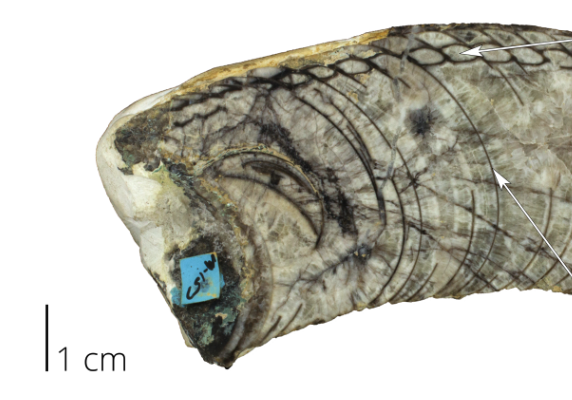

Question
What structure is indicated by the top arrow? What structure is indicated by the bottom arrow?
Answer
The top arrow indicates the siphuncle. The bottom arrow indicates a single septum.
Question
All living Coleiodea are active predators, with a single known exception. What is that exception?
Answer
The vampire squid. This species (Vampyroteuthis infernalis) uses a long filament to feed on detritus suspended in seawater.
Question
When did the ammonoids go extinct?
Answer
At the end of the Cretaceous period (=end of the Mesozoic era).
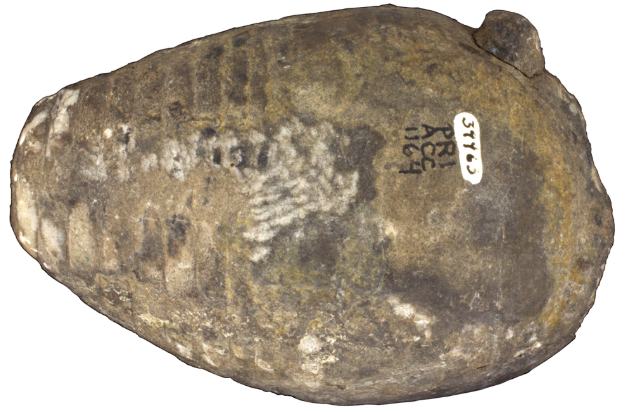

Question
Characterize the shape of the shell above.
Answer
Shell is an orthoconic brevicone (=straight, short shell).
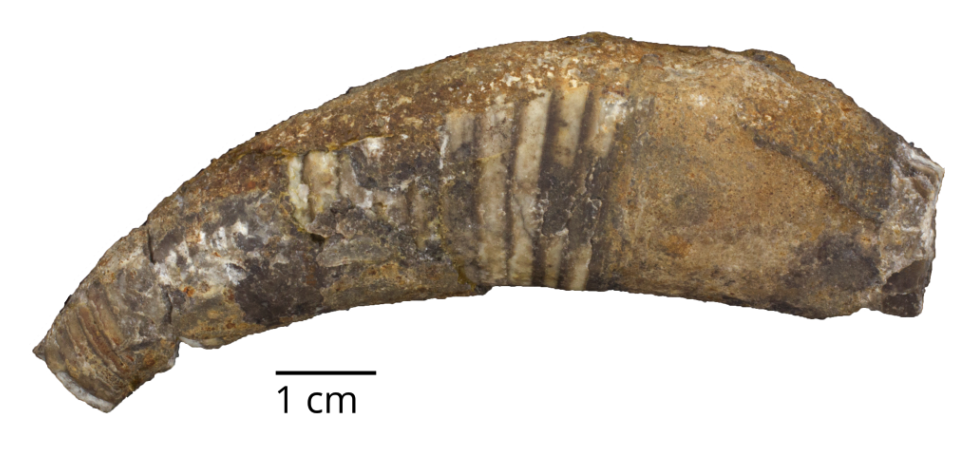

Question
Characterize the shape of the cephalopod shell above.
Answer
The shell is a cyrtoconic longicone (=curved, long shell).
Question
Which one of the following IS NOT a feature shared by all cephalopods? a) Beak b) Arms c) External shell d) Funnel
Answer
c) External shell. Coleoids do not have external shells, though cuttlefish have an internal shell, as did belemnites.
Question
During which geological period did Nautiloidea and Coleoidea--the two major groups of extant Cephalopoda--likely diverge from one another?
Answer
Nautiloidea and Coleoidea are thought to have diverged from one another during the Devonian period. In other words, the shared common ancestor of the modern chambered nautilus and a squid lived during the Devonian.
Question
True or False: Cephalopods with ceratite sutures are completely extinct.
Answer
True. Some ammonoids had ceratitic sutures (especially during the Triassic period), but all ammonoids are now extinct.
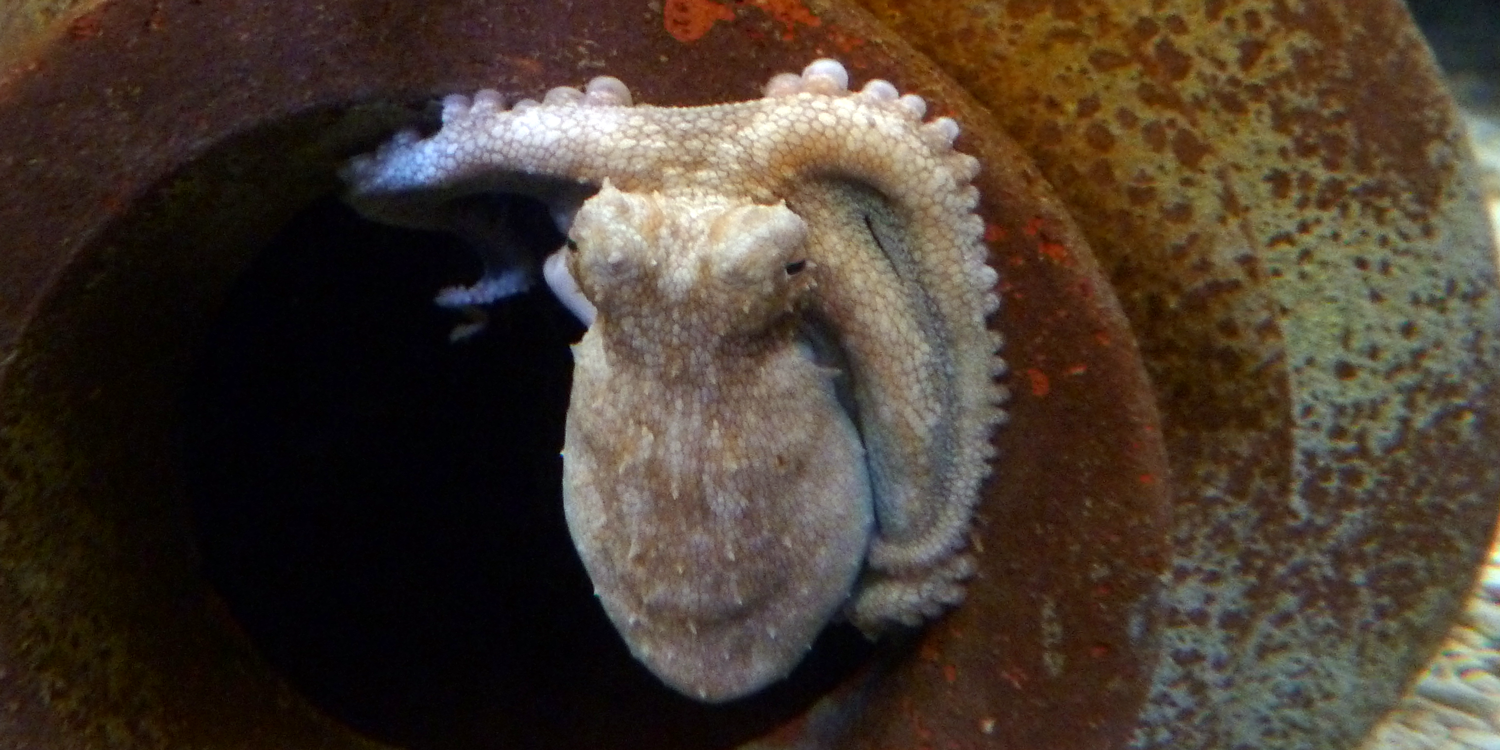

Question
To which major group of cephalopods do octopuses belong?
Answer
Octopuses are coleoids. More specifically, they belong to the group of coleoids called Octopodiformes. Cuttlefish, squids, and belemnites are also coleoids.
Question
Which one of the following is an example a member of the Decapodiformes? a) Nautilus. b) Ammonite. c) Squid. d) Octopus.
Answer
c) Decapodiformes. The name means ten feet; squids and cuttlefish both have ten arms and are part of this clade.
Usage

Unless otherwise indicated, the written and visual content on this page is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. This page was written by Jonathan R. Hendricks. See captions of individual images for attributions. See original source material for licenses associated with video and/or 3D model content.



